Data management functionalities, like a data table, can be safely attributed to core parts of modern business apps. DHTMLX JavaScript Grid component helps developers speed up the implementation of feature-packed data tables for efficient data analysis. The modern UI of our Grid, which has intuitive features and smooth rendering of complex datasets, ensures a high usability level on various devices. But with the advent of AI technologies, there are new great opportunities to bring the user experience to a new level. For instance, what if your data grid could analyze text on its own, transforming it into structured, ready-to-use data?
That’s exactly what we’re going to implement in this guide. You will learn how to create a smart system that reads customer reviews, figures out the sentiment, pulls out important tags, and writes a quick summary for each one using DHTMLX Grid and the OpenAI API.
Preparatory Step
Before we proceed to concrete steps on embedding AI functionality into DHTMLX Grid, you need the following:
- Installed Node.js to run the backend server
- An API key from an AI provider
Note: this tutorial uses OpenAI for the AI part, but you can easily replace it with other services such as Google (Gemini models), Anthropic (Claude models), Mistral, etc., without changing much of the backend logic.
Here’s a quick look at the expected result:
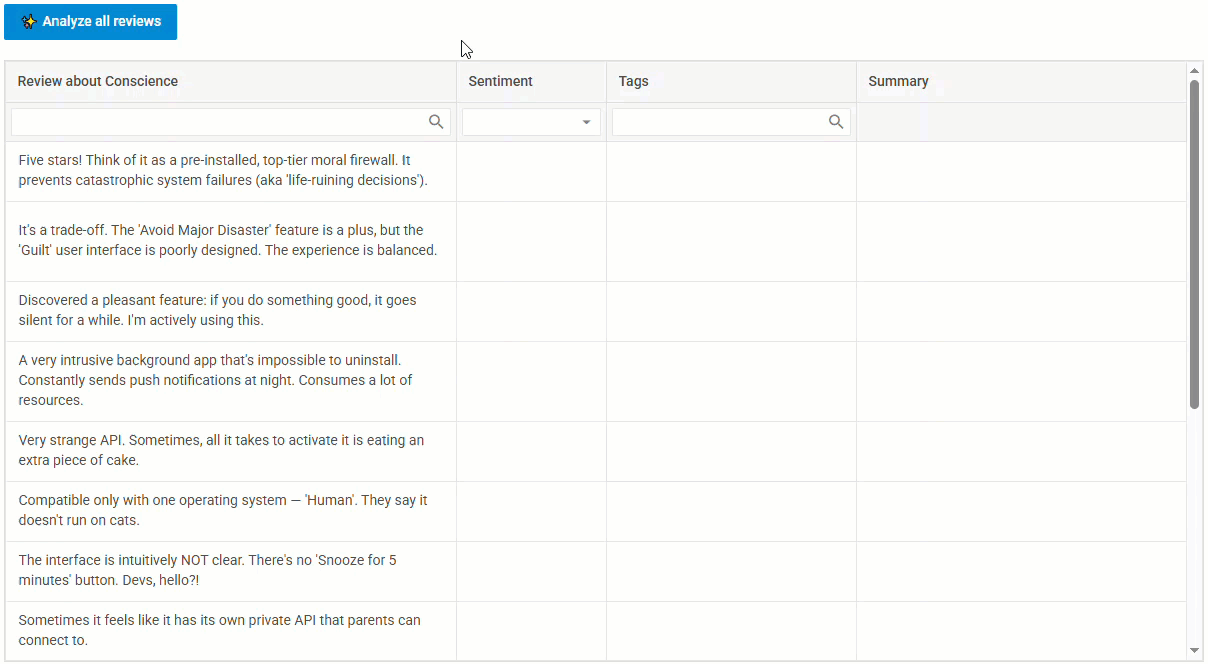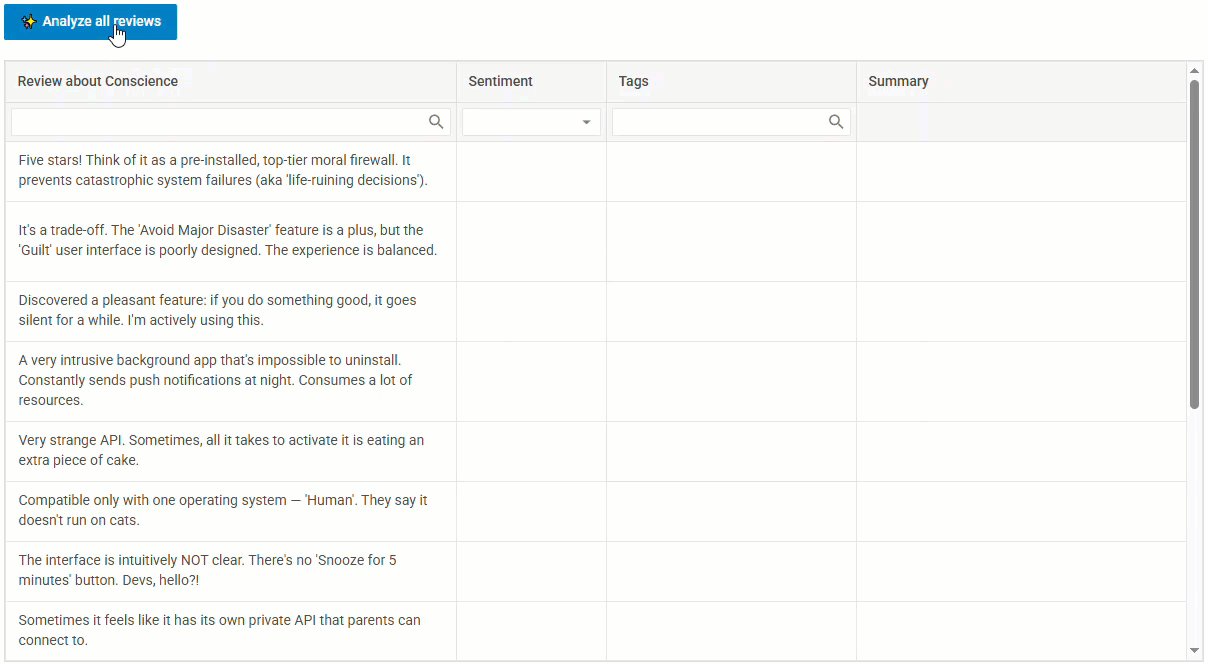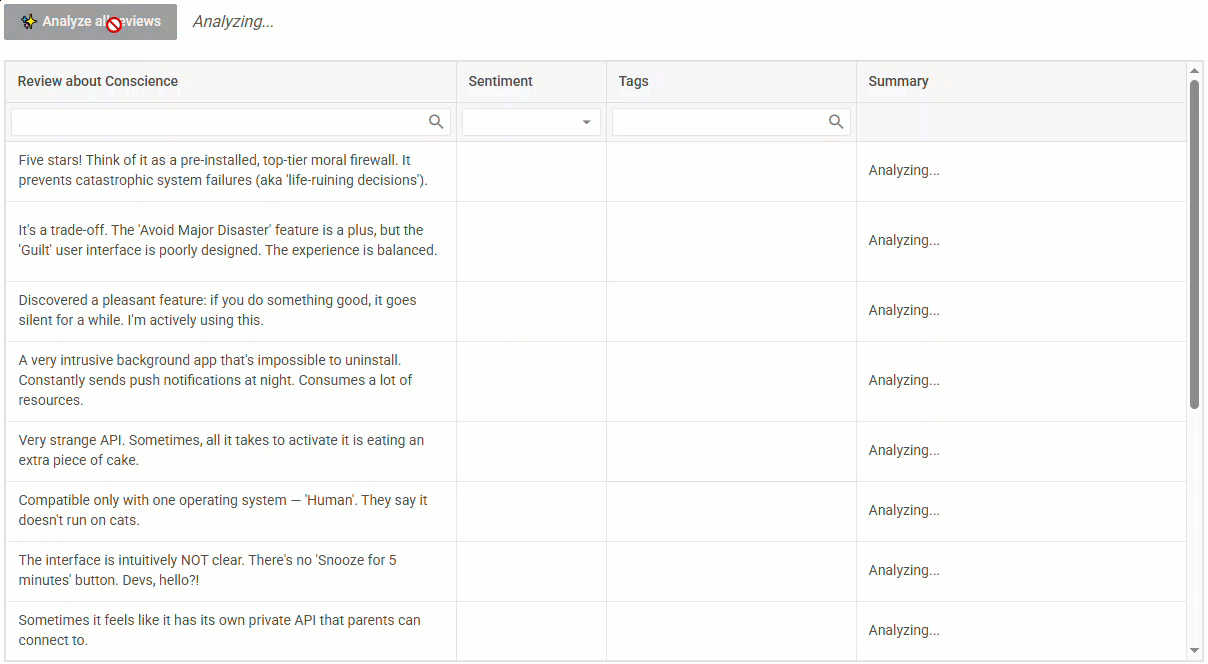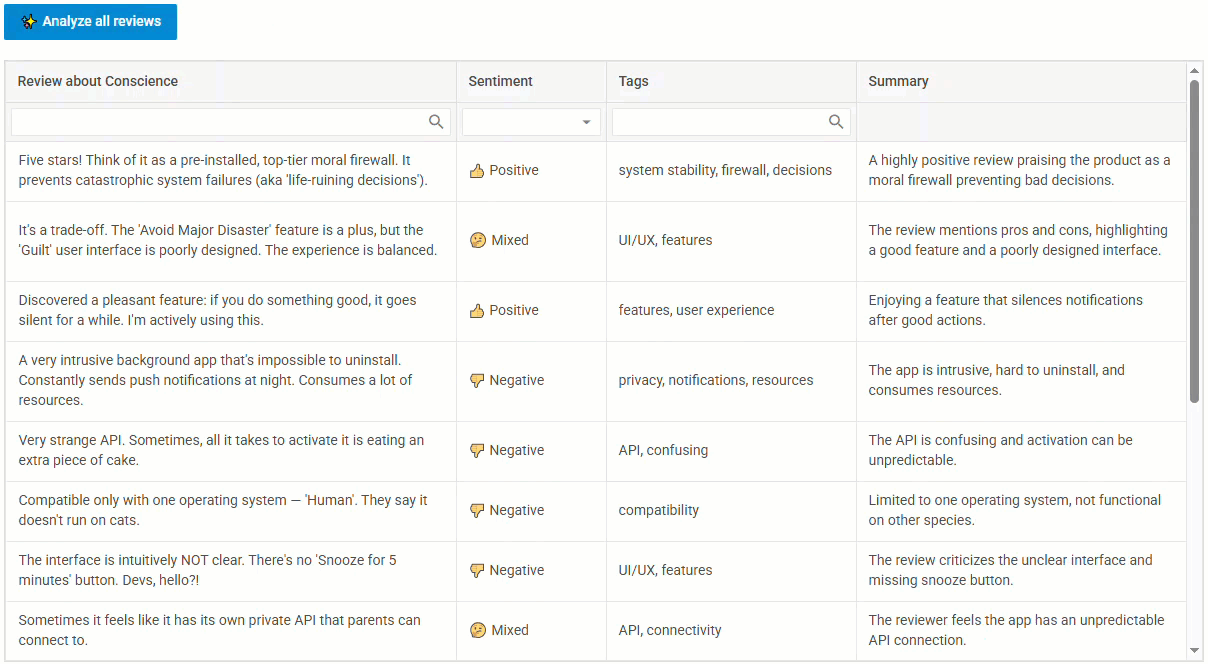
In this demo, you can paste in raw text, hit the “Analyze all reviews” button, and watch as the AI fills in the empty fields in real time.
If you want to look under the hood, check the complete project on GitHub.
Now, let us go through the main steps required to implement a similar integration on the web.
Step 1: Setting Up DHTMLX Grid
Let’s start by putting together a simple web page with the initialized Grid. There is nothing complicated here:
- Create an HTML file (index.html), where you’ll include source files + Socket.io for server communication
<html>
<head>
<title>DHTMLX Grid + AI Analysis</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.dhtmlx.com/suite/pro/edge/suite.css">
<script src="https://cdn.dhtmlx.com/suite/pro/edge/suite.js"></script>
<!-- We'll need Socket.io for server communication, so let's include it now. -->
<script src="/socket.io/socket.io.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>Customer Review Analysis with AI</h1>
<button id="analyze-btn">Analyze all reviews</button>
<div id="grid"></div>
</div>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
- Prepare the initial data, initialize the Grid in the app.js file, and load the data into it:
// 1. Raw data (IDs + reviews)
const gridData = [
{ id: 1, review_text: "Five stars! It prevents catastrophic system failures (aka 'life-ruining decisions').", sentiment: "", tags: "", summary: "" },
{ id: 2, review_text: "The 'Avoid Major Disaster' feature is a plus, but the 'Guilt' user interface is poorly designed.", sentiment: "", tags: "", summary: "" },
{ id: 3, review_text: "A very intrusive background app that's impossible to uninstall. Constantly sends push notifications at night.", sentiment: "", tags: "", summary: "" }
// ... and other reviews
];
// 2. Now, initialize the Grid widget
const grid = new dhx.Grid("grid", {
columns: [
// The review column is editable
{ id: "review_text", header: [{ text: "Review" }], editable: true, width: 450 },
// These columns will be populated by the AI
{
id: "sentiment",
header: [{ text: "Sentiment" }],
// Use a template for a more appealing display
template: (text) => {
if (text === 'positive') return '👍 Positive';
if (text === 'negative') return '👎 Negative';
if (text === 'neutral') return '😐 Neutral';
if (text === 'mixed') return '🤔 Mixed';
return text;
}
},
{ id: "tags", header: [{ text: "Tags" }], width: 250 },
{ id: "summary", header: [{ text: "Summary" }] },
],
data: gridData, // Load the data
autoWidth: true,
autoHeight: true
});
});
As a result, you’ll get a data table with the reviews displayed in there. The “Sentiment,” “Tags,” and “Summary” columns will still be empty at this point. That’s where the AI comes in next.
Step 2: Enabling AI-Powered Analysis in the Grid
After adding the reviews to the table, it is time to trigger their analysis. There are two possible analysis scenarios:
- Bulk analysis – when a user clicks the “Analyze all reviews” button
- Single analysis – immediately after a user edits the text of a review in its cell
But first, you need to establish communication between your app and the server (which takes care of the OpenAI requests). To do that, you can use WebSockets via the Socket.IO library. It will help ensure real-time updates between the client and server parts of the app.
Here is how it all looks in the app.js file:
// Establish a connection to the server
const socket = io();
socket.on('connect', () => console.log("Successfully connected to the server!"));
const analyzeButton = document.getElementById("analyze-btn");
// Scenario 1: Bulk analysis on button click
analyzeButton.addEventListener('click', () => {
// Get all rows that haven't been analyzed yet (i.e., have no summary)
const reviewsToAnalyze = grid.data.serialize()
.filter(row => row.review_text && !row.summary)
.map(row => ({ id: row.id, text: row.review_text }));
if (reviewsToAnalyze.length > 0) {
// Send the array of reviews to the server
socket.emit('analyze_bulk_reviews', reviewsToAnalyze);
}
});
// Scenario 2: Single row analysis after an edit
grid.events.on("afterEditEnd", (value, row, column) => {
// Fire only if the "review_text" column was changed
if (column.id === "review_text") {
const reviewData = { id: row.id, text: row.review_text };
// Send a single review to the server for instant analysis
socket.emit('analyze_single_review', reviewData, (response) => {
// Process the immediate response from the server
updateGridRow(response.payload);
});
}
});
The key things here are:
- grid.data.serialize() retrieves data from the grid table
- afterEditEnd event is a hook for reacting to user input
Together, they give you two natural entry points for submitting data to the backend.
Also, you’ll need a special helper function (updateGridRow) for updating the table with new content:
if (!analysis) return;
const tagsString = Array.isArray(analysis.tags) ? analysis.tags.join(', ') : analysis.tags;
// This is a key DHTMLX Grid method!
// It finds a row by its ID and updates its cells with new data.
grid.data.update(analysis.id, {
sentiment: analysis.sentiment,
tags: tagsString,
summary: analysis.summary
});
}
Step 3: Receiving Results and Updating the Grid
The successful sending of data to the server is only half the battle, as you have yet to handle the response. When the AI sends the review_analyzed event back, you need to receive it and update the right row.
This is where the updateGridRow function steps in and calls grid.data.update(id, data). It is a go-to option for updating rows in the Grid on the fly.
For this purpose, you add a handler in app.js:
// Listen for an event from the server with analysis results
socket.on('review_analyzed', (response) => {
if (response.status === 'success') {
updateGridRow(response.payload);
} else {
// If an error occurred, let the user know
grid.data.update(response.id, { summary: "Error during analysis." });
console.error(`Analysis failed for ID ${response.id}: ${response.message}`);
}
});
With this in place, the grid updates instantly without the need for reloading.
Step 4: Working on AI Responses
The key step on the backend is to enable the AI functionality. We won’t dive into every single line of code here (the full example is on GitHub), but the main trick is how you ask the AI for particular data.
A simple “analyze this” prompt won’t do the trick. Instead, you can take advantage of Tool Calling. This technique allows specifying the structure of responses expected from AI.
Here is what to do next:
- You give AI its main instruction (system prompt). To put it simply, you tell AI that it plays the role of a data analysis assistant responsible for sentiment, tags, and summary fields.
function getSystemPrompt() {
return `You are an AI assistant for data analysis. Your task is to analyze customer reviews. For each review, determine:
1. **sentiment**: 'positive', 'negative', 'neutral', or 'mixed'.
2. **tags**: 2-4 keywords (e.g., 'bugs', 'resources', 'notifications', 'UI/UX').
3. **summary**: a very brief summary of the review in English.
Always use the provided 'update_grid_with_analysis' function to return the result.`;
}
- Using the Tool Schema definition, you provide a blueprint for the JSON structure the AI must return.
export const schemaList = [{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "update_grid_with_analysis",
description: "Accepts an array of analyzed reviews and returns them to update the grid.",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
analyzed_rows: {
type: "array",
items: {
type: "object",
properties: {
id: { type: ["string", "number"], description: "The ID of the row in the grid." },
sentiment: { type: "string", enum: ["positive", "negative", "neutral", "mixed"] },
tags: { type: "array", items: { type: "string" } },
summary: { type: "string", description: "A very brief summary of the review." }
},
required: ["id", "sentiment", "tags", "summary"]
}
}
},
required: ["analyzed_rows"]
}
}
}];
Thus, you make sure that AI sticks to the expected format instead of making things up, thereby providing valid results.
That’s it. You’ve connected the modern interface of DHTMLX Grid with AI to make data analysis smoother and more practical. For more technical details, check out the full backend code on GitHub.
Wrapping Up
Integrating DHTMLX Grid with AI-based capabilities opens up new opportunities for ensuring an enjoyable user experience with datasets of any complexity. The same pattern can be used for many other goals: classifying support tickets, enriching user profiles, or finding trends in comments. Learn more about DHTMLX Grid in the documentation and download a free 30-day trial version of this widget to test its capabilities in real-world scenarios.